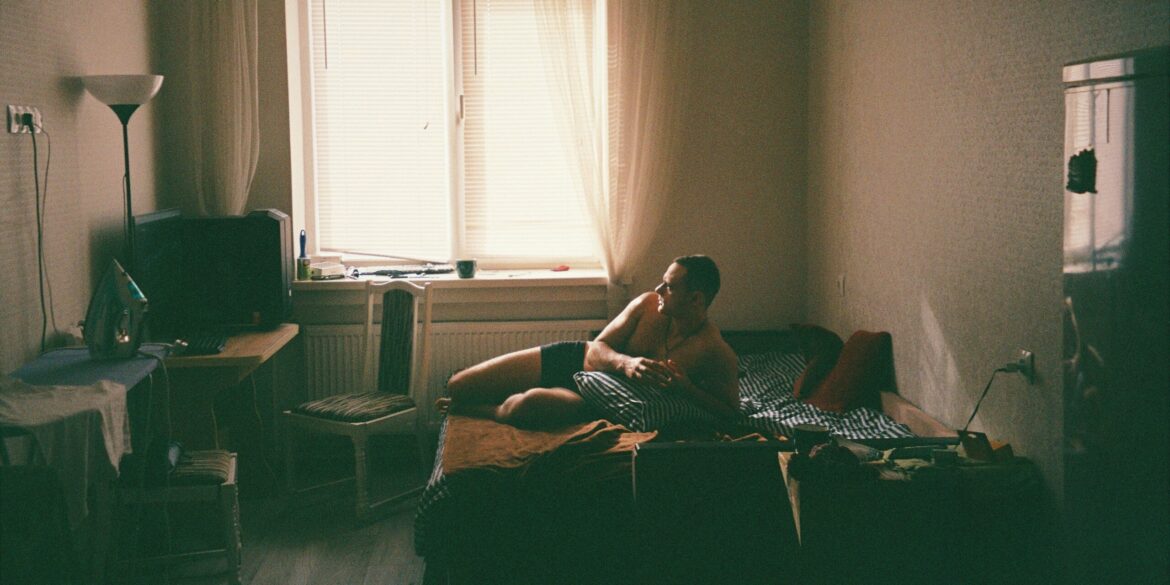
The U.S. Census Bureau released new data on May 29, 2025, highlighting a notable increase in the number of single men living alone in both urban and suburban areas across the country. According to the latest figures, there has been a 12% rise in this demographic compared to the previous census cycle. Experts attribute this trend to a combination of demographic shifts, changing cultural attitudes toward independence, delayed marriage, and evolving housing preferences.
This increase in single men living alone is not only a reflection of broader societal transformations but also a factor influencing various sectors such as housing markets, consumer behavior, and social services designed specifically for men. Analysts point to the growing preference for autonomy and individual lifestyles, which has been accelerated by shifts in work-from-home policies that became widespread during and after the COVID-19 pandemic.
Demographers explain that delayed marriage and changes in traditional family structures have played a crucial role in this trend. Many men in their late 20s and 30s are choosing to remain single longer or prioritize career and personal growth over early family formation. In addition, cultural acceptance of solo living has grown, reducing the social stigma historically associated with living alone.
Housing experts note that this demographic shift is prompting changes in the real estate market. There is increased demand for smaller, affordable housing units suitable for single occupancy. Urban planners and developers are paying closer attention to this growing segment of residents who seek convenient, well-located apartments or condos that cater to their lifestyle.
Consumer behavior also reflects these changes. Single men living alone tend to have distinct spending patterns compared to other household types. They often allocate more resources toward entertainment, technology, dining out, and personal wellness. This has led businesses to adjust marketing strategies and product offerings to meet the preferences of this demographic.
The Census Bureau’s report further emphasizes the implications for social services and community support networks. Mental health professionals and social workers highlight that living alone can sometimes lead to increased feelings of isolation and loneliness, which have become growing concerns in modern society. Community engagement initiatives aimed at fostering social connectivity among solo-living men are gaining importance, with programs designed to encourage participation in group activities, volunteer work, and social clubs.
Public health experts stress that these support networks can play a critical role in improving the well-being of men living alone, offering both emotional support and practical resources. The rise in single-person households also calls for tailored approaches in healthcare, including addressing unique health risks and promoting preventive care.
Sociologists and cultural commentators suggest that this trend toward solo living among men is part of a broader shift in societal norms related to work, relationships, and lifestyle. The post-pandemic era has reshaped many aspects of daily life, including the way people view home, community, and personal space. The flexibility of remote work arrangements has allowed more individuals to prioritize where and how they live, often choosing independence over traditional family settings.
In summary, the U.S. Census Bureau’s findings shed light on a significant social evolution with wide-reaching effects on housing, economics, and public health. Policymakers, urban developers, and social service providers are urged to recognize and address the unique needs of the growing population of single men living alone. By fostering inclusive communities and expanding support systems, society can better adapt to these ongoing demographic and cultural shifts.