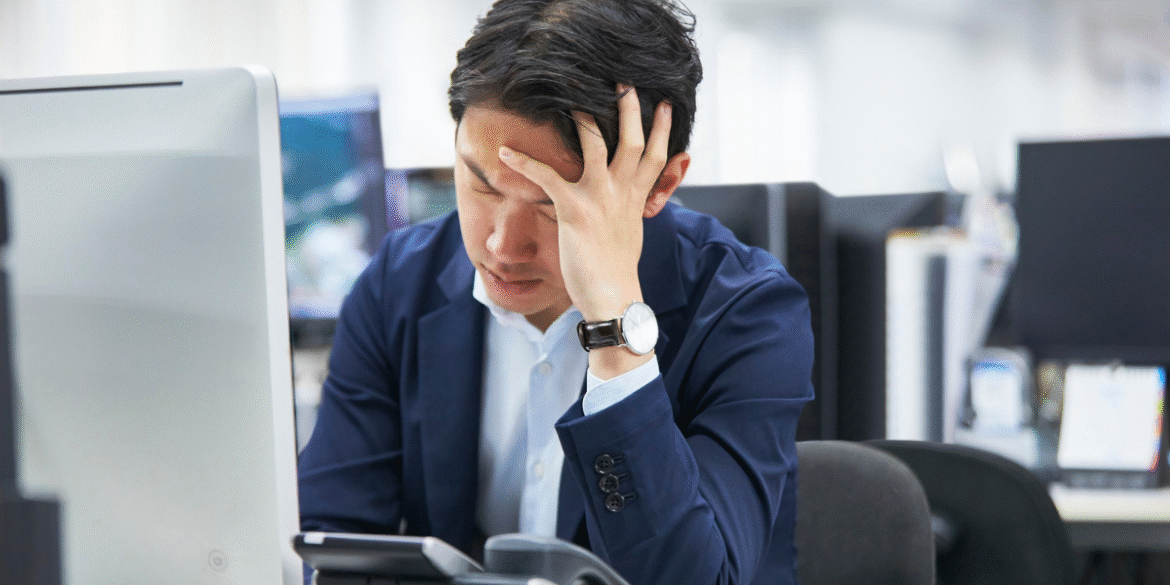
June 15, 2022, marked a significant point in the ongoing conversation about workplace stress and its disproportionate effects on men. As industries such as technology, finance, and healthcare became increasingly high-pressure environments, men in these sectors were found to be particularly vulnerable to the consequences of chronic stress. The long-term effects of this stress were becoming more evident, not only in terms of physical health but also in terms of emotional and mental well-being. This growing concern led to an increased focus on workplace wellness programs and the implementation of strategies aimed at reducing stress among male employees.
For years, workplace stress has been recognized as a global concern, affecting employees of all genders. However, research from June 2022 underscored a significant pattern: men working in demanding environments were at a higher risk for developing serious health conditions linked to chronic stress. A report released by the American Psychological Association (APA) revealed that, among male workers, the likelihood of suffering from heart disease, mental health disorders, and burnout was notably higher in high-stress work settings. Industries such as technology, finance, and healthcare, known for their fast-paced, results-oriented cultures, were identified as particularly stressful for men.
The American Psychological Association’s report from June 2022 emphasized the connection between stress and health risks among men, noting that the physiological effects of stress, such as elevated blood pressure, disrupted sleep patterns, and increased susceptibility to heart disease, were becoming more prevalent. Stress was also linked to a range of mental health challenges, including anxiety and depression, which were found to significantly affect men’s overall well-being and job performance.
Adding to these concerns, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) corroborated these findings by pointing out that stress was not only impacting men’s physical health but was also leading to emotional strain. Men, especially those in leadership positions or demanding professions, often felt the pressure to perform at high levels, and societal expectations that men should exhibit strength and resilience made it harder for many to seek help or express vulnerability. As a result, stress went unaddressed, contributing to deteriorating mental health, which in turn affected both personal and professional lives.
The pandemic further exacerbated these issues, with remote work becoming a major shift in workplace dynamics. While remote work offered flexibility, it also blurred the boundaries between personal and professional life, making it more challenging for employees, particularly men, to disconnect and manage their stress. This new work environment created a double-edged sword, where men found themselves working longer hours, experiencing increased expectations, and struggling with the lack of in-person support from coworkers or managers.
In light of the mounting evidence on the negative impact of stress on male workers, companies across industries started to take notice. As a result, workplace wellness programs became a key focus for many organizations looking to support their employees’ health and well-being. Mindfulness practices, stress management workshops, and mental health resources became more widely available, helping to address the root causes of stress in the workplace.
Several organizations introduced wellness programs that provided male employees with tools to manage stress effectively. These programs included stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, and regular mental health check-ins with counselors. In addition, companies began to focus on creating a culture of support and openness where employees felt more comfortable discussing stress-related concerns. By prioritizing these initiatives, businesses hoped to alleviate the burden of workplace stress and foster healthier, more resilient teams.
Mindfulness practices, in particular, were promoted as effective tools to reduce stress and improve focus, clarity, and overall well-being. These practices encouraged employees to slow down, reflect on their mental and emotional state, and gain better control over their reactions to stressful situations. Many companies also implemented policies that prioritized work-life balance, offering flexible hours and remote work options that allowed employees to manage their stress in a healthier way.
Furthermore, mental health resources, such as access to counseling services, employee assistance programs (EAPs), and workshops on stress management, were rolled out to help employees cope with workplace pressures. This support system was designed to help men break through the stigma of asking for help and ensure they had access to the resources they needed to maintain their mental and physical health.
As the year progressed, the conversation surrounding workplace stress continued to evolve, with a growing recognition of the need to address the unique pressures faced by male employees. The hope was that, by focusing on mental health and well-being, organizations could help reduce the risks associated with chronic stress and improve overall productivity. This approach not only benefits employees but also contributes to a healthier workplace culture that values the health of its workforce.
In conclusion, June 15, 2022, marked an important turning point in recognizing the harmful effects of workplace stress, particularly among men in high-pressure industries. As the evidence of stress’s long-term health consequences became more apparent, companies across various sectors began implementing wellness programs aimed at reducing stress and improving mental well-being. These efforts were not only about improving the health of employees but also about fostering a culture where stress management and mental health support were prioritized, ultimately leading to healthier, more productive workplaces.