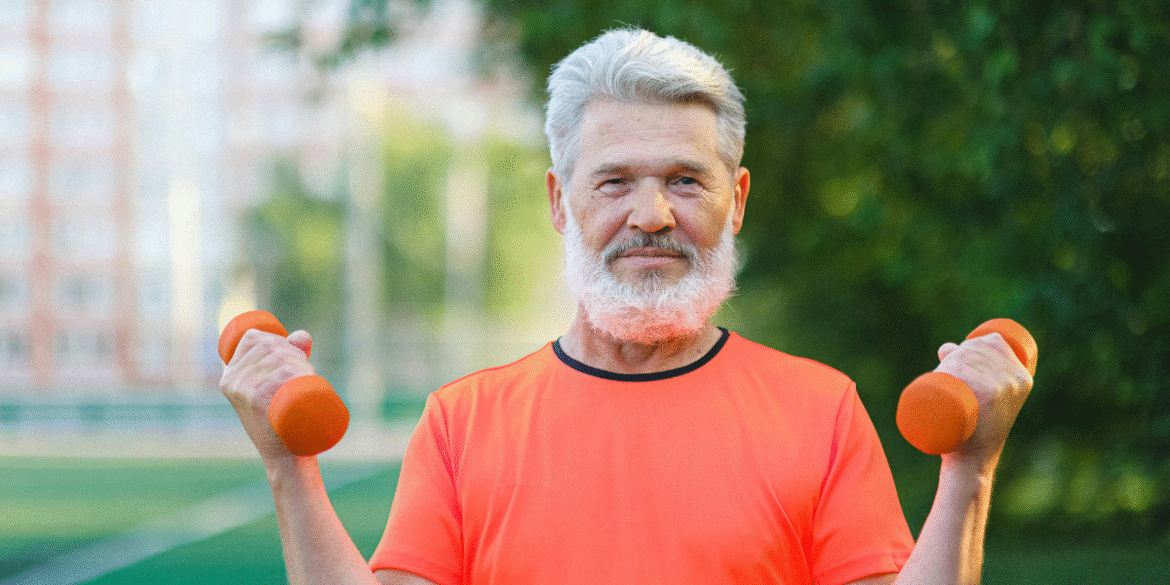
May 15, 2022, saw a significant rise in the discussion surrounding strength training for men over 40, emphasizing the importance of weight training in maintaining health and enhancing longevity as men age. This growing focus on fitness for older adults highlights how regular strength training can have far-reaching benefits, including maintaining muscle mass and preventing the decline in physical function that typically occurs with aging.
Strength Training and Aging in Men
As men age, they often face challenges related to muscle loss, decreased bone density, and the onset of chronic conditions like heart disease and diabetes. However, recent studies have shown that strength training is an effective strategy to mitigate these risks. For men over 40, incorporating regular resistance exercises into their fitness routines can be a powerful tool in not only maintaining muscle mass but also enhancing overall health.
One of the most significant benefits of strength training is its ability to combat sarcopenia, the gradual loss of muscle mass that occurs as people age. This condition not only affects strength but can also have a profound impact on mobility and quality of life. Regular resistance training can help slow the progression of sarcopenia, allowing men to preserve functional strength and improve their ability to perform daily tasks.
Additionally, strength training has been shown to increase bone density, which is especially important for aging men, who are at an increased risk for osteoporosis. By placing stress on bones through weight-bearing exercises, strength training stimulates bone-building processes, helping to reduce the risk of fractures and maintain bone health over time. This benefit is particularly crucial for men over 40, as bone mass begins to naturally decline in their 40s and 50s.
Reducing the Risk of Chronic Diseases
Beyond its effects on muscle and bone health, strength training also plays a key role in reducing the risk of chronic diseases. For men over 40, conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome become increasingly common. However, research has shown that strength training can significantly reduce the risk of these conditions by improving cardiovascular health, enhancing insulin sensitivity, and lowering inflammation in the body.
Strength training can also help control body weight and reduce abdominal fat, which is linked to an increased risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes. By boosting metabolism and increasing muscle mass, strength training improves the body’s ability to burn calories and regulate fat storage. This is particularly important for aging men, who often experience a slower metabolism and increased difficulty maintaining a healthy weight.
The cardiovascular benefits of strength training are particularly noteworthy. Regular resistance exercise has been shown to lower blood pressure, reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol, and improve overall heart health. These benefits are essential for men over 40, as cardiovascular disease is a leading cause of death among older men. Engaging in strength training can help counteract some of the effects of aging on the heart and reduce the likelihood of developing heart-related issues later in life.
Mental Health Benefits of Strength Training
The benefits of strength training extend beyond physical health and can have a profound impact on mental well-being. Many men experience mental health challenges as they age, including increased stress, anxiety, and depression. Strength training provides a powerful antidote to these issues by releasing endorphins, the body’s natural mood boosters.
In addition to improving mood, strength training also enhances cognitive function. Research suggests that regular resistance exercise can improve brain health by stimulating the growth of new neurons and increasing blood flow to the brain. For men over 40, maintaining mental sharpness is crucial, and strength training may play a role in preventing age-related cognitive decline, such as the early stages of dementia or Alzheimer’s disease.
Furthermore, the sense of accomplishment that comes with successfully completing a strength training session can help boost self-esteem and improve confidence. For aging men, this psychological benefit can be particularly significant, as it reinforces their ability to maintain control over their health and fitness as they grow older.
Fitness Programs for Older Men
As the importance of strength training for aging men becomes more widely recognized, specialized fitness programs have emerged to cater specifically to this demographic. These programs are designed with the unique needs of older adults in mind, focusing on exercises that promote strength, flexibility, and balance while minimizing the risk of injury.
Such programs often involve gradual, progressive resistance training, which allows men to build strength at a safe and manageable pace. They typically incorporate exercises that target the major muscle groups while also emphasizing functional movements that enhance mobility and coordination. These programs can be found at many fitness centers and gyms, with certified trainers who have expertise in working with older adults to ensure that participants exercise safely and effectively.
In addition, many fitness centers now offer group classes tailored to older men, fostering a supportive environment where participants can work together to improve their health and fitness. The social aspect of these classes also adds an extra layer of motivation, as individuals are more likely to stick with a workout routine when they have the support of others.
Conclusion
Incorporating strength training into the lives of men over 40 is a proven strategy to not only preserve muscle mass but also improve overall health, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, and promote mental well-being. With the growing availability of tailored fitness programs, older men now have access to safe, effective workouts that address their unique health needs. The benefits of strength training extend far beyond physical appearance, impacting virtually every aspect of health and well-being as men age.